Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with "= How to control the Builtin LED MicroPython = this is GPIO6 (D13 in Arduino) <syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> from machine import Pin from time import sleep # u..." |
No edit summary |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A simple IDE to program [[MicroPython]] on the board is the [[Arduino Lab for MicroPython]] IDE. Alternatives are, [[Jupyter Notebook]] or [[Thonny IDE]]. | |||
= Upgrade the Arduino Firmware = | |||
* Reinstall the MicroPython Firmware (version 1.22.2 tested) | |||
* Install the [[Arduino IDE]] | |||
* Start Arduino IDE and select the Arduino RP2040 board | |||
* Go to Tools -> Firmware Update -> Check updates and select version 1.5.0 and press Install | |||
= Install the MicroPython Firmware = | |||
<b>Note:</b> Before installing [[MicroPython]] ensure you have the latest Arduino Firmware, see [[Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect#Upgrade the Arduino Firmware|Upgrade the Arduino Firmware]]. | |||
* Download the firmware for the Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect from https://micropython.org/download/ARDUINO_NANO_RP2040_CONNECT/ | |||
* Unplug the board from the computer. | |||
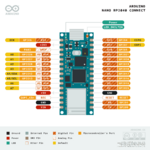
* Force the board in bootloader mode by connecting GND and REC pin with a wire: https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/nano-rp2040-connect/rp2040-openmv-setup/ | |||
[[File:Arduino01a.jpg|x150px]] [[File:Bootpin.jpg|x150px]] [[File:Pinout-nano.png|x150px]] | |||
* Plug the board into the USB port on your computer, it appears as a drive in your filesystem | |||
[[File:Drive01.png|200px]] | |||
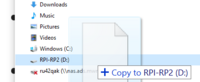
* Remove the wire between the GND and REC pin (before you copy the file onto the device) | |||
* Copy the firmware you downloaded on the drive that showed up in your file system | |||
[[File:file-copy.PNG|200px]] | |||
* Once it is completely copied to the device, unplug the board and plug in again | |||
[[File:Arduino02a.PNG|200px]] | |||
* Now you should be able to use Arduino Lab for the Micropython development environment: https://labs.arduino.cc/en/labs/micropython | |||
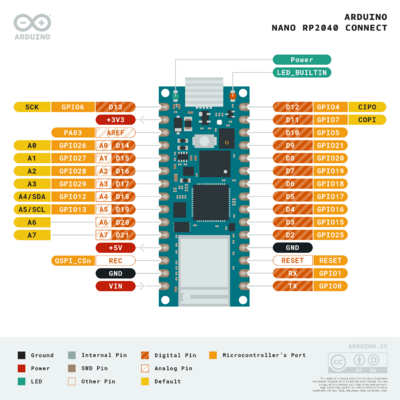
= Pinout = | |||
[[File:Pinout-nano.png|400px]] | |||
= How to control the Builtin LED MicroPython = | = How to control the Builtin LED MicroPython = | ||
this is GPIO6 (D13 in Arduino) | this is GPIO6 (D13 in Arduino) | ||
| Line 16: | Line 53: | ||
myLED.off() | myLED.off() | ||
sleep(0.5) | sleep(0.5) | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== Example: Read Accelerometer and Gyro === | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> | |||
import time | |||
from lsm6dsox import LSM6DSOX | |||
from machine import Pin, I2C | |||
lsm = LSM6DSOX(I2C(0, scl=Pin(13), sda=Pin(12))) | |||
while (True): | |||
accel_data = lsm.accel() | |||
print('Accelerometer: x:{:>8.3f} y:{:>8.3f} z:{:>8.3f}'.format(*accel_data)) | |||
gyro_data = lsm.gyro() | |||
print('Gyroscope: x:{:>8.3f} y:{:>8.3f} z:{:>8.3f}'.format(*gyro_data)) | |||
print("") | |||
time.sleep_ms(100) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 100: | Line 154: | ||
conn.close() | conn.close() | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==External links== | |||
* https://docs.arduino.cc/learn/programming/arduino-and-python | |||
* https://docs.arduino.cc/hardware/nano-rp2040-connect | |||
* https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/nano-rp2040-connect/rp2040-python-api#imu-lsm6dsox | |||
* https://github.com/openmv/openmv/blob/918ccb937730cc759ee5709df089d9de516dc7bf/scripts/libraries/lsm6dsox.py | |||
[[Category:Microcontrollers]] | |||
[[Category:Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:49, 14 June 2024
A simple IDE to program MicroPython on the board is the Arduino Lab for MicroPython IDE. Alternatives are, Jupyter Notebook or Thonny IDE.
Upgrade the Arduino Firmware
- Reinstall the MicroPython Firmware (version 1.22.2 tested)
- Install the Arduino IDE
- Start Arduino IDE and select the Arduino RP2040 board
- Go to Tools -> Firmware Update -> Check updates and select version 1.5.0 and press Install
Install the MicroPython Firmware
Note: Before installing MicroPython ensure you have the latest Arduino Firmware, see Upgrade the Arduino Firmware.
- Download the firmware for the Arduino Nano RP2040 Connect from https://micropython.org/download/ARDUINO_NANO_RP2040_CONNECT/
- Unplug the board from the computer.
- Force the board in bootloader mode by connecting GND and REC pin with a wire: https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/nano-rp2040-connect/rp2040-openmv-setup/
- Plug the board into the USB port on your computer, it appears as a drive in your filesystem
- Remove the wire between the GND and REC pin (before you copy the file onto the device)
- Copy the firmware you downloaded on the drive that showed up in your file system
- Once it is completely copied to the device, unplug the board and plug in again
- Now you should be able to use Arduino Lab for the Micropython development environment: https://labs.arduino.cc/en/labs/micropython
Pinout
How to control the Builtin LED MicroPython
this is GPIO6 (D13 in Arduino)
from machine import Pin
from time import sleep
# using the internal LED on the Pico - pin 25
myLED = Pin(6, Pin.OUT)
while True:
# this switches the LED on for 1 second
myLED.on()
sleep(0.1)
# this switches the LED off for 500 ms
myLED.off()
sleep(0.5)Example: Read Accelerometer and Gyro
import time
from lsm6dsox import LSM6DSOX
from machine import Pin, I2C
lsm = LSM6DSOX(I2C(0, scl=Pin(13), sda=Pin(12)))
while (True):
accel_data = lsm.accel()
print('Accelerometer: x:{:>8.3f} y:{:>8.3f} z:{:>8.3f}'.format(*accel_data))
gyro_data = lsm.gyro()
print('Gyroscope: x:{:>8.3f} y:{:>8.3f} z:{:>8.3f}'.format(*gyro_data))
print("")
time.sleep_ms(100)
Example of a WIFI-Access Point and Webserver to control the LED
# Wi-Fi AP Mode Example
#
# This example shows how to use Wi-Fi in Access Point mode.
# this version by Albrecht Schmidt, https://www.sketching-with-hardware.org/wiki/
# based on the following examples:
# https://randomnerdtutorials.com/esp32-esp8266-micropython-web-server/
# https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/nano-rp2040-connect/rp2040-python-api
import network, socket, time
from machine import Pin
led = Pin(6, Pin.OUT) #on board LED
SSID ='Nano_RP2040_Connect_test' # Network SSID
KEY ='12345678' # Network key (should be 8 chars) - for real use, choose a safe one
HOST = ''
PORT = 80 # 80 ist the http standard port, can also use non-privileged port e.g. 8080
# Init wlan module and connect to network
wlan = network.WLAN(network.AP_IF)
wlan.active(True)
# it seems in this version the AP mode only supports WEP
wlan.config(essid=SSID, key=KEY, security=wlan.WEP, channel=2)
print("AP mode started. SSID: {} IP: {}".format(SSID, wlan.ifconfig()[0]))
# create the webpage with a button to toggle the LED
def web_page():
if led.value() == 1:
led_state="ON"
else:
led_state="OFF"
html ="""<html><head>
<title>Nano RP2040 Connnect Web Server</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" href="data:,">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Nano RP2040 Connnect </1>
<h2>Web Server Test</h2>
<p>LED state: <strong>""" + led_state + """</strong></p><p><a href="/?led=on"><button class="button">ON</button></a></p>
<p><a href="/?led=off"><button class="button button2">OFF</button></a></p>
</body>
</html>"""
return html
# get started with setting up the sever sockedt
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Bind and listen
server.bind([HOST, PORT])
server.listen(5)
# loop to deal with http requests
while True:
conn, addr = server.accept()
print('Connection from %s' % str(addr))
request = conn.recv(1024)
request = str(request)
print('Request Content = %s' % request)
# check if the request includes led=on or off
led_on = request.find('/?led=on')
led_off = request.find('/?led=off')
# request is 'GET /?led=on' or 'GET /?led=off' - the string starts at position 6 (counting starts at 0)
if led_on == 6:
print('LED ON')
led.value(1)
if led_off == 6:
print('LED OFF')
led.value(0)
response = web_page()
conn.send('HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n')
conn.send('Content-Type: text/html\n')
conn.send('Connection: close\n\n')
conn.send(response)
conn.close()External links
- https://docs.arduino.cc/learn/programming/arduino-and-python
- https://docs.arduino.cc/hardware/nano-rp2040-connect
- https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/nano-rp2040-connect/rp2040-python-api#imu-lsm6dsox
- https://github.com/openmv/openmv/blob/918ccb937730cc759ee5709df089d9de516dc7bf/scripts/libraries/lsm6dsox.py