SG90 Servo: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
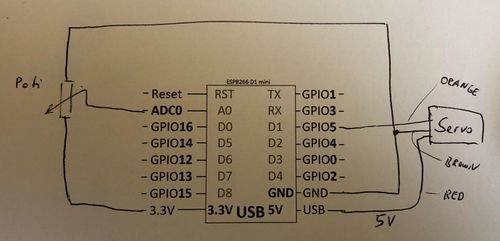
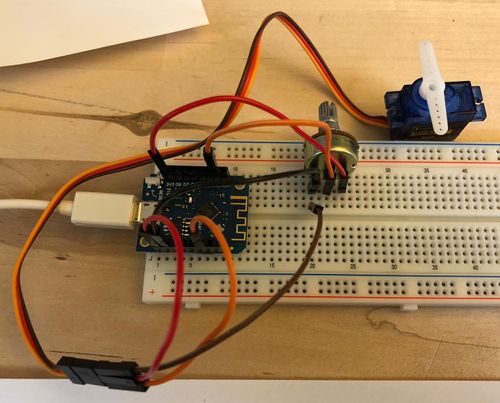
= Schematic - Connecting the SG90 = | = Schematic - Connecting the SG90 = | ||
[[File:Servo00.jpg|500px]] | |||
[[File:Servo01.jpg|500px]] | |||
= Code Example ESP8266 = | = Code Example ESP8266 = | ||
Revision as of 00:58, 22 December 2020
IMPORTANT
In many computers the current is not enough to drive the servo!!!
If it does not work, keeps disconnecting, or rebooting the ESP the power is not sufficent and you need an extra power supply.
Schematic - Connecting the SG90
Code Example ESP8266
A0 is the analog input with 10 bit resolution. It reads the analog value every second and print it to the console and sets the servo based on the analog input.
from machine import Pin, ADC, PWM
from time import sleep
analogPin = ADC(0)
servoPin = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
pwm = PWM(servoPin, freq=50)
pwm.deinit()
pwm = PWM(servoPin, freq=50)
while True:
analogVal = analogPin.read()
pwm.duty(int(analogVal/10))
print(analogVal)
sleep(1)