LDR: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
analogVal = analogPin.read() | analogVal = analogPin.read() | ||
print(analogVal) | print(analogVal) | ||
sleep(1) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
== Code Example Arduino Nano Connect RP2040 == | |||
A0 is the analog input with 16 bit resolution. It reads the analog value every second and print it to the console- | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> | |||
#Example usage for Arduino Nano | |||
from machine import Pin, ADC | |||
from time import sleep | |||
analogPin = ADC(Pin(26)) | |||
while True: | |||
analogVal16 = analogPin.read_u16() | |||
print(analogVal16) | |||
sleep(1) | sleep(1) | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 11:30, 2 June 2024
Description
An LDR is a light-dependent resistor. It changes it's resistance depending on the light falling onto the LDR.
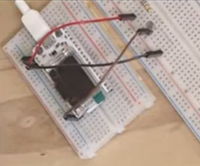
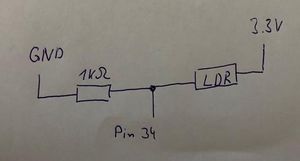
How to connect it electrically
Connecting the light dependent resistor (LDR). The value you read is dependent on how bright it is.
How to control it in MicroPython
This makes Pin 34 an analog input and set it to 12 bit. It reads the analog value every second and print it to the console.
#Example usage for ESP32
from machine import Pin, ADC
from time import sleep
analogPin = ADC(Pin(34))
analogPin.atten(ADC.ATTN_11DB)
while True:
analogVal = analogPin.read()
print(analogVal)
sleep(1)
Code Example Arduino Nano Connect RP2040
A0 is the analog input with 16 bit resolution. It reads the analog value every second and print it to the console-
#Example usage for Arduino Nano
from machine import Pin, ADC
from time import sleep
analogPin = ADC(Pin(26))
while True:
analogVal16 = analogPin.read_u16()
print(analogVal16)
sleep(1)Related Tutorial Videos