Analog Joystick: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with "= Description = The analog joystick includes 2 Potentiometer and one digital switch. It has 5 connectors: * GND - connected to GND * 5V - which is in our cases connected..." |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
= How to connect it electrically = | = How to connect it electrically = | ||
[[File: | [[File:File:Joystick-electro.JPG|x400px]] | ||
= How to control it in MicroPython = | = How to control it in MicroPython = | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 29 August 2020
Description
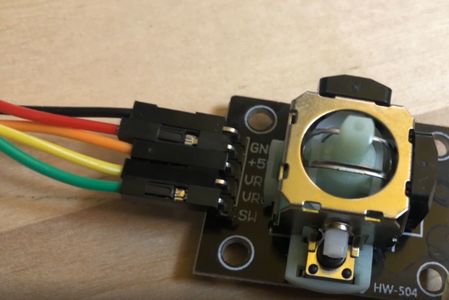
The analog joystick includes 2 Potentiometer and one digital switch.
It has 5 connectors:
- GND - connected to GND
- 5V - which is in our cases connected to 3.3V
- VRx - the voltage representing the position in X
- VRy - the voltage representing the position in Y
- SW - 0 if pressed
How to connect it electrically
File:File:Joystick-electro.JPG
How to control it in MicroPython
Basic code to generate a 500 Hz signal
reading all values and printing them to the console
#Example usage for ESP32
from machine import Pin, ADC
from time import sleep
# analog inputs for X and Y
analogPinX = ADC(Pin(34))
analogPinY = ADC(Pin(35))
#switching the analog input to 12Bit (0...4095)
analogPinX.atten(ADC.ATTN_11DB)
analogPinY.atten(ADC.ATTN_11DB)
# digital input on pin 26
sw = Pin(26, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP) # enable internal pull-up resistor
while True:
analogValX = analogPinX.read()
analogValY = analogPinY.read()
switch = sw.value()
print("x:%s y:%s sw:%s" % (analogValX, analogValY, switch))
sleep(1)Related Tutorial Videos