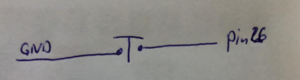Difference between revisions of "Push button"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "= Description = Text Image(s) = How to connect it electrically = Text Image(s) = How to control it in MicroPython = <syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> # todo #...") |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Description = | = Description = | ||
| − | + | With a button we can select which of the two sides are connected to the middle. It is similar to a [[switch]] but it only stays in the state as long as it is pressed. | |
| − | + | [[File:Button02.PNG|x200px]] | |
| + | = How to connect it electrically = | ||
| + | This is the most simple way of connecting a button. if the button is not pressed (open) there is no signal at the pin. Hence here we should use an internal pullup resistor. | ||
| − | + | [[File:Button01.PNG|300px]] | |
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
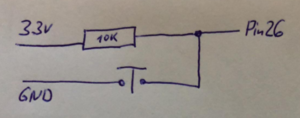
| + | This is the connection of a button with a pullup resistor. If the button is not pressed, 3.3V are connected to the pin via the 10 KOhm resistor (reads 1). if it is pressed it is connected to GND (reads 0). | ||
| − | + | [[File:Pullup02.PNG|300px]] | |
= How to control it in MicroPython = | = How to control it in MicroPython = | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Simple digital read on pin 26 with internal Pull-up == | ||
| + | Not all pins have internal pull-up resistors. On the ESP32 Webkit GPIO32, GPIO33, ..., GPIO39 are input only and they do not have internal pull-ups or pull-down resistors. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> | <syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> | ||
| − | + | from machine import Pin | |
| − | + | in26 = Pin(26, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP) | |
| + | print(in26.value()) | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | = | + | == Simple digital read on pin 26 == |
<syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> | <syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> | ||
| − | + | from machine import Pin | |
| − | + | in26 = Pin(26, Pin.IN) | |
| + | print(in26.value()) | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Related Tutorial Videos = | = Related Tutorial Videos = | ||
| − | + | Digital Input | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <youtube>va1beT6sxLs</youtube> | |
Latest revision as of 00:18, 30 August 2020
Contents
Description[edit]
With a button we can select which of the two sides are connected to the middle. It is similar to a switch but it only stays in the state as long as it is pressed.
How to connect it electrically[edit]
This is the most simple way of connecting a button. if the button is not pressed (open) there is no signal at the pin. Hence here we should use an internal pullup resistor.
This is the connection of a button with a pullup resistor. If the button is not pressed, 3.3V are connected to the pin via the 10 KOhm resistor (reads 1). if it is pressed it is connected to GND (reads 0).
How to control it in MicroPython[edit]
Simple digital read on pin 26 with internal Pull-up[edit]
Not all pins have internal pull-up resistors. On the ESP32 Webkit GPIO32, GPIO33, ..., GPIO39 are input only and they do not have internal pull-ups or pull-down resistors.
1 from machine import Pin
2 in26 = Pin(26, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
3 print(in26.value())
Simple digital read on pin 26[edit]
1 from machine import Pin
2 in26 = Pin(26, Pin.IN)
3 print(in26.value())
Related Tutorial Videos[edit]
Digital Input