Difference between revisions of "RGB LED"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
= How to connect it electrically = | = How to connect it electrically = | ||
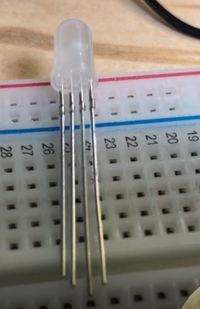
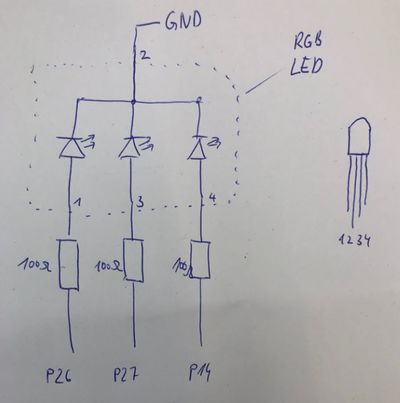
The RGB LED is connected like 3 paralell LEDs. It is important that you need one resistor for each color! The resistor goes before the LED and not onto the common ground. | The RGB LED is connected like 3 paralell LEDs. It is important that you need one resistor for each color! The resistor goes before the LED and not onto the common ground. | ||
| + | There are different types - the one we use has a common ground, but there are also versions with common +. | ||
[[File:RgbIMG 9775.jpg|400px]] | [[File:RgbIMG 9775.jpg|400px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= How to control it in MicroPython = | = How to control it in MicroPython = | ||
Latest revision as of 00:07, 20 August 2020
Contents
Description[edit]
A regular RGB LED is basically 3 LEDs (one red, one green, one blue) in parallel. This is not a smart LED, for smart LEDs see LED Ring NeoPixel.
How to connect it electrically[edit]
The RGB LED is connected like 3 paralell LEDs. It is important that you need one resistor for each color! The resistor goes before the LED and not onto the common ground. There are different types - the one we use has a common ground, but there are also versions with common +.
How to control it in MicroPython[edit]
Switching indiviual color on and off
1 from machine import Pin
2
3 blue = Pin(26, Pin.OUT)
4 green = Pin(27, Pin.OUT)
5 red = Pin(14, Pin.OUT)
6
7 blue.on()
8 green.off()
9 red.off()
Controlling intensity
1 from machine import Pin, PWM
2
3 blue = PWM(Pin(26))
4 green = PWM(Pin(27))
5 red = PWM(Pin(14))
6
7 # set PWM frequency to 1000Hz
8 blue.freq(1000)
9 green.freq(1000)
10 red.freq(1000)
11
12 # have blue on at about 50% intesity
13 blue.duty(512)
14 green.duty(0)
15 red.duty(0)
16
17 # have red and green at full intesity (mixed color)
18 blue.duty(0)
19 green.duty(1023)
20 red.duty(1023)
A small Program in MicroPython[edit]
1 from machine import Pin, PWM
2 from time import sleep
3
4 # connect it to Pin 26, 27, and 14
5 blue = PWM(Pin(26))
6 green = PWM(Pin(27))
7 red = PWM(Pin(14))
8
9 # base frequency for PWM is 1000Hz
10 blue.freq(1000)
11 green.freq(1000)
12 red.freq(1000)
13
14 # this is a function to allows to give an "RGB"-Color to the LED
15 # duty take an argument from 0 to 2023... by multiplying the 0..255 by 4 we get 0 to 2020 - which seems close enough
16 def rgb(r=255,g=255,b=255):
17 blue.duty(b*4) # set duty cycle
18 green.duty(g*4) # set duty cycle
19 red.duty(r*4) # set duty cycle
20
21 # show some cases....
22 while True:
23 rgb(255,255,255) # white
24 sleep(1)
25 rgb(0,0,0) # off = black
26 sleep(1)
27 rgb(255,0,0) # red
28 sleep(1)
29 rgb(0,255,0) # gree
30 sleep(1)
31 rgb(0,0,255) # blue
32 sleep(1)
Related Tutorial Videos[edit]
In this part of the tutorial, we show how to connect an RGB-LED and programming it with Micropython. We first look at what an RGB LED is by building one with 3 separate LEDs. We then look at switching it on and off and how to set the color using the duty cycle in the PWM output.
Background[edit]
text
image(s)