Difference between revisions of "SG90 Servo"
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''In many computers the current is not enough to drive the servo!!!''' | '''In many computers the current is not enough to drive the servo!!!''' | ||
| − | '''If it does not work, keeps disconnecting, or rebooting the ESP the power is not sufficent and you need an extra power supply.''' | + | '''If it does not work, keeps disconnecting, or rebooting the ESP the power is not sufficent and you need a capacitor ot an extra power supply.''' |
| + | |||
| + | See the last section below ([[SG90 Servo#Power Issues]]) and the video for details how to do this. | ||
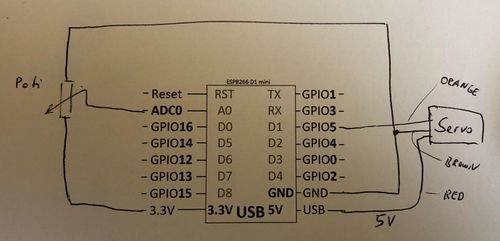
= Schematic - Connecting the SG90 = | = Schematic - Connecting the SG90 = | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
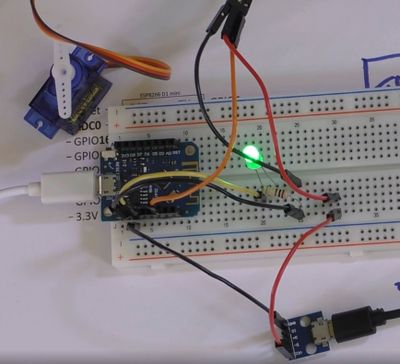
[[File:Servo01.jpg|500px]] | [[File:Servo01.jpg|500px]] | ||
| − | = Code | + | = Code Examples ESP8266 = |
| + | |||
| + | = Basic control = | ||
| + | Assuming the servo is connected to Pin 5. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="python" line='line'> | ||
| + | from machine import Pin,PWM | ||
| + | from time import sleep | ||
| + | |||
| + | servoPin = Pin(5, Pin.OUT) | ||
| + | pwm = PWM(servoPin, freq=50) | ||
| + | pwm.deinit() # workaround to reset PWM | ||
| + | pwm = PWM(servoPin, freq=50) | ||
| + | |||
| + | val = 50 | ||
| + | |||
| + | while True: | ||
| + | pwm.duty(val) | ||
| + | val = val + 1 | ||
| + | if val>100: | ||
| + | val = 50 | ||
| + | print(val) | ||
| + | sleep(0.05) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
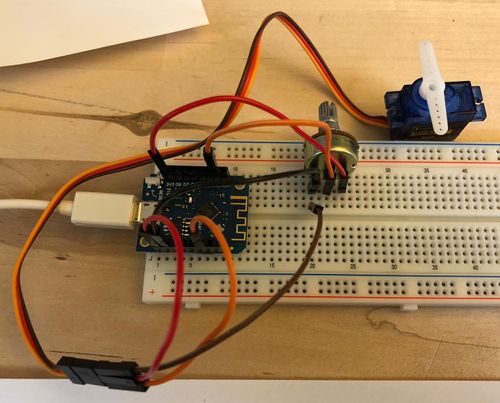
| + | = Controlling the servo with a Poti = | ||
A0 is the analog input with 10 bit resolution. It reads the analog value every second and print it to the console and sets the servo based on the analog input. | A0 is the analog input with 10 bit resolution. It reads the analog value every second and print it to the console and sets the servo based on the analog input. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 56: | ||
sleep(1) | sleep(1) | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Related Tutorial Videos = | ||
| + | == PWM Output: connecting a servo and and LED == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>XovIHYo7s1A</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- old video <youtube>_4bXk8JjQSk</youtube> --> | ||
| + | |||
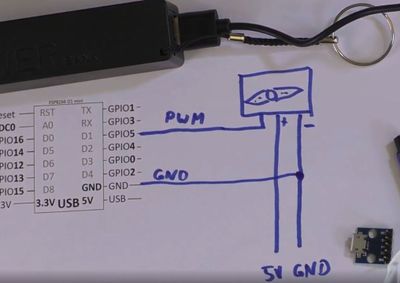
| + | = Power Issues = | ||
| + | When connecting the servo to the ESP32 or ESP8266 it may not work at all, may restart at random times, or may move to a wrong angle. This is typically a power issue. The ESP-board is and the USB-output of the computer does not provide enough power. | ||
| + | There are two fixes: adding a big capacitor (e.g. electrolytic capacitor [[Elko]] 2000 uF) or adding an external power source (e.g. [[USB-Power]]). The external power source is the better solution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Have a look at the video for details. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Adding a Capacitor == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:PowerElko.JPG|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Connecting an external Power Source == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:PowerUSB.JPG|400px]] | ||
| + | [[File:PowerUSB-module.JPG|270px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:PowerUSB-setup.JPG|400px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:25, 30 December 2020
Contents
IMPORTANT[edit]
In many computers the current is not enough to drive the servo!!!
If it does not work, keeps disconnecting, or rebooting the ESP the power is not sufficent and you need a capacitor ot an extra power supply.
See the last section below (SG90 Servo#Power Issues) and the video for details how to do this.
Schematic - Connecting the SG90[edit]
Code Examples ESP8266[edit]
Basic control[edit]
Assuming the servo is connected to Pin 5.
1 from machine import Pin,PWM
2 from time import sleep
3
4 servoPin = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
5 pwm = PWM(servoPin, freq=50)
6 pwm.deinit() # workaround to reset PWM
7 pwm = PWM(servoPin, freq=50)
8
9 val = 50
10
11 while True:
12 pwm.duty(val)
13 val = val + 1
14 if val>100:
15 val = 50
16 print(val)
17 sleep(0.05)
Controlling the servo with a Poti[edit]
A0 is the analog input with 10 bit resolution. It reads the analog value every second and print it to the console and sets the servo based on the analog input.
1 from machine import Pin, ADC, PWM
2 from time import sleep
3
4 analogPin = ADC(0)
5 servoPin = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
6 pwm = PWM(servoPin, freq=50)
7 pwm.deinit()
8 pwm = PWM(servoPin, freq=50)
9
10 while True:
11 analogVal = analogPin.read()
12 pwm.duty(int(analogVal/10))
13 print(analogVal)
14 sleep(1)
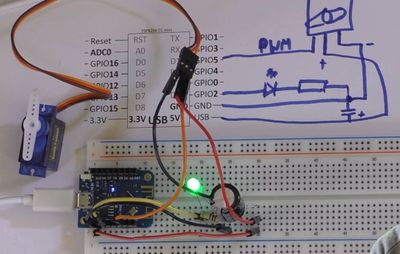
Related Tutorial Videos[edit]
PWM Output: connecting a servo and and LED[edit]
Power Issues[edit]
When connecting the servo to the ESP32 or ESP8266 it may not work at all, may restart at random times, or may move to a wrong angle. This is typically a power issue. The ESP-board is and the USB-output of the computer does not provide enough power. There are two fixes: adding a big capacitor (e.g. electrolytic capacitor Elko 2000 uF) or adding an external power source (e.g. USB-Power). The external power source is the better solution.
Have a look at the video for details.